taylor series ln x|how to find taylor series : Cebu Setting c = 0 gives the Maclaurin Series of f(x): ∞ ∑ n = 0f ( n) (0) n! xn. The difference between a Taylor polynomial and a Taylor series is the former is a . Resultado da An IP is a unique address of a server on the internet. Similar to how a telephone number allows you to connect to a specific phone on the telecom network, similarly, an IP address allows your computer to connect to a specific server on the internet.
0 · what is the best approximation for input value when fxg
1 · taylor series lnx
2 · taylor series for log x
3 · taylor series expansion of ln x
4 · taylor polynomial of ln x
5 · ln x series expansion
6 · how to find taylor series
7 · cos x taylor series expansion
Resultado da Play Jigsaw Puzzle online for free. Enjoy a stylish & modern version of timeless game. Play the game online or download for Mac™, Windows™, .
taylor series ln x*******Setting c = 0 gives the Maclaurin Series of f(x): ∞ ∑ n = 0f ( n) (0) n! xn. The difference between a Taylor polynomial and a Taylor series is the former is a .
Pictured is an accurate approximation of sin x around the point x = 0. The pink curve is a polynomial of degree seven: The error in this approximation is no more than |x| / 9!. For a full cycle centered at the origin (−π < x < π) the error is less than 0.08215. In particular, for −1 < x < 1, the error is less than 0.000003.
$$f(x)=\ln(x).$$ The Taylor expansion around $a$ is $$f(x)=\sum_{n=0}^{\infty} \frac{f^{(n)}(a)}{n!}(x-a)^n,$$ so for $a = 1$, $$f'(x) = .
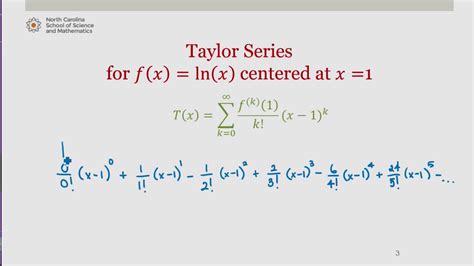
Taylor Series for f (x)=ln (x) Centered at x=1. This is part of series of videos developed by Mathematics faculty at the North Carolina School of Science and .
Taylor Series. A calculator for finding the expansion and form of the Taylor Series of a given function. To find the Maclaurin Series simply set your Point to zero (0). Get the .how to find taylor seriesThe supposed correct answers are: $$\ln(1+x) = \int \left(\frac{1}{1+x}\right)dx$$ $$\ln(1+x) = \sum_{k=0}^{\infty} \int (-x)^k dx$$Representing Functions with Taylor and Maclaurin Series. We now discuss issues of convergence for Taylor series. We begin by showing how to find a Taylor series for a .
In this section we will discuss how to find the Taylor/Maclaurin Series for a function. This will work for a much wider variety of function than the method discussed in .taylor series of ln (x) Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals.Taylor Series: ln x. Save Copy. Log InorSign Up. . x − 1 − x − 1 2 2 + x − 1 3 3 − x − 1 4 4 + x − 1 5 5 − x − 1 6 6 + x − 1 7 7 − x − 1 8 8 + x − 1 9 9 6. x . Calculus: Taylor Expansion of sin(x) example. Calculus: Integrals. example. Calculus: Integral with adjustable bounds.
The Taylor series is used in mathematics to approximate a function. Gain a better understanding of the Taylor series expression with a detailed, step-by-step example using the function ln(1+x).
Sep 10, 2014. Any Taylor series of a function f (x) can be found by calculating. ∞ ∑ n=0 f n(a) ⋅ (x −a)n n! where a is the point where you need to approximate the function. Let's say you need to approximate ln(x) around the point x = 1. So: The Taylor series of degree 0 is simply f (1) = ln(1) = 0. The Taylor series of degree 1 is the .To determine if a Taylor series converges, we need to look at its sequence of partial sums. These partial sums are finite polynomials, . Figure 6.5 The function y = ln x y = ln x and the Taylor polynomials p 0, p 1, p 2 p 0, p 1, p 2 and p 3 p 3 at x = 1 x = 1 are plotted on this graph. Checkpoint 6.10. Find the Taylor polynomials p 0, p 1, p . $\begingroup$ So the question : calculate Limit using Taylor-series $\frac{\ln(x)}{x}$ is wrong? where $\lim{x \to 0}$ $\endgroup$ – Khan Saab. Commented Jan 24, 2017 at 16:59. 1 $\begingroup$ That limit doesn't exist - $|ln(x)|$ tends to infinty, as does $1/x$, so the limit is not defined. $\endgroup$ Calculus: We derive the Taylor series for f(x) = ln(x) at x = 1 and use the 4th Taylor polynomial to estimate ln(.9). We then apply Taylor's Theorem to obt.taylor series of ln (x) Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music..taylor series ln xConvergence of Taylor series. Given an infinitely differentiable function f(x) with Taylor series (at a) P∞ bn(x − a)n either P∞. n=0 n=0 bn(x − a)n converges and is equal to f(x) for every number x or there is a number R (called the radius of convergence) for which P∞ bn(x − a)n converges and is n=0 equal to f(x) for |x − a| < R .
Taylor Series Expansions In this short note, a list of well-known Taylor series expansions is provided. We focus on Taylor series about the point x = 0, the so-called Maclaurin series. In all cases, the interval of convergence is indicated. The variable x is real. We begin with the infinite geometric series: 1 1− x = X∞ n=0 xn, |x| < 1. (1) Find the \(n^\text{th}\) Taylor polynomial of \(y=\ln x\) at \(x=1\). Use \(p_6(x)\) to approximate the value of \(\ln 1.5\). Use \(p_6(x)\) to approximate the value of \(\ln 2\). Solution. . we explore Taylor Series, where we represent a function with an infinite series. Contributors and Attributions. Gregory Hartman (Virginia Military . 7.5: Working with Taylor Series is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. In this section we show how to use those Taylor series to derive Taylor series for other functions. We then present two common applications of power series. First, we show how power series can be ..Our aim is to find a good polynomal approximation to the curve in the region near x = 10. We need to use the Taylor Series with a = 10. The first term in the Taylor Series is f(a). In this example, `f(a)` ` = f(10) = ln 10 = 2. 302\ 585\ 093.` Now for the derivatives. Recall the derivative of ln x, which is `1/x`. So `f'(x)=1/x` The general formula for the Taylor series of a function f (x) around x = 1 is: f (x) = ∞ ∑ n=0 f (n)(1) n! (x − 1)n. we can immediately note that: f (0)(1) = lnx ∣x=1 = 0. so the constant term is null. For the following terms, we have to calculate the derivatives of f (x) = lnx for all orders: d dx lnx = 1 x = x−1.
Using the definition of Taylor expansion f(z) ≈ f(a) + df ( z) dz |z = a(z − a), where here z = 1 − x, f(z) = ln(1 − z) and a = 1. I know you can get ln(1 − x) ≈ − x by e.g. substitute x → − x into the expansion of and through other methods etc. But I still don't quite get how you can get the minus sign from Taylor expansion .
Common Functions Expressed as Taylor Series. At this point, we have derived Maclaurin series for exponential, trigonometric, and logarithmic functions, as well as functions of the form \( f(x)=(1+x)^r\).taylor series ln x how to find taylor seriesOur aim is to find a good polynomal approximation to the curve in the region near x = 10. We need to use the Taylor Series with a = 10. The first term in the Taylor Series is f(a). In this example, `f(a)` ` = f(10) = ln 10 = 2. 302\ 585\ 093.` Now for the derivatives. Recall the derivative of ln x, which is `1/x`. So `f'(x)=1/x` The general formula for the Taylor series of a function f (x) around x = 1 is: f (x) = ∞ ∑ n=0 f (n)(1) n! (x − 1)n. we can immediately note that: f (0)(1) = lnx ∣x=1 = 0. so the constant term is null. For the following terms, we have to calculate the derivatives of f (x) = lnx for all orders: d dx lnx = 1 x = x−1.

Using the definition of Taylor expansion f(z) ≈ f(a) + df ( z) dz |z = a(z − a), where here z = 1 − x, f(z) = ln(1 − z) and a = 1. I know you can get ln(1 − x) ≈ − x by e.g. substitute x → − x into the expansion of and through other methods etc. But I still don't quite get how you can get the minus sign from Taylor expansion . About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright . Putting all of the terms together, we get the third-degree Taylor polynomial.???\ln{6}+\frac{1}{3}(x-3)-\frac{1}{18}(x-3)^2+\frac{1}{81}(x-3)^3??? Power series representation. We want to find a power series representation for .Example: another useful Taylor series. Find the Taylor series expansion of \( \ln(1+x) \) to third order about \( x=0 \). If you're following along at home, try it yourself before you keep reading! This is the key piece that we'll need to go back and finish our projectiles with air resistance calculation. Therefore, we can write the answer as. ln(2) + 1 2(x − 2) − 1 8(x −2)2 + 1 24(x −2)3 − 1 64(x − 2)4 + ⋯. This series happens to equal ln(x) for 0 < x < 4 (the "radius of convergence" is 2 and it equals the function for these values as well). First, we can start with the general definition of the Taylor series expansion, which is . If x = 0, then this series is known as the Maclaurin series for f. Definition 5.3.1: Maclaurin and Taylor series. If f has derivatives of all orders at x = a, then the Taylor series for the function f at a is. ∞ ∑ n = 0f ( n) (a) n! (x − a)n = f(a) + f′ (a)(x − a) + f ″ (a) 2! (x − a)2 + ⋯ + f ( n) (a) n! (x − a)n + ⋯.For convenience we restate Taylor’s Theorem 8.4.1. Theorem 8.4.1: Taylor’s Theorem (Taylor Series) Suppose f(z) is an analytic function in a region A. Let z0 ∈ A. Then, f(z) = ∞ ∑ n = 0an(z − z0)n, where the series converges on any disk | z − z0 | < r contained in A. Furthermore, we have formulas for the coefficients.Expansions Which Have Logarithm-Based Equivalents. Summantion Expansion: Equivalent Value: Comments: x n This screencast has been created with Explain Everything™ Interactive Whiteboard for iPad
Resultado da 27 de jul. de 2012 · Step Up Revolution: Directed by Scott Speer. With Cleopatra Coleman, Ryan Guzman, Misha Gabriel Hamilton, Michael .
taylor series ln x|how to find taylor series